Google Ranking Factors
How to Improve Google SEO Ranking – Increasing SEO Ranking to Dominate Google
Here is a complete list of google ranking factors. By following these more than 200 google ranking factors, you can improve google seo ranking which lets your website found easily on google. If you work on these seo ranking factors alone, you can take advantage of our free seo tools at http://seo1seotools.com and http://free-backlinks.net
. If you want to get professional help to improve your website’s google seo ranking, you can go to our website at http://seo-san-jose.net. We are located in San Jose, the capital of Silicon Valley. We are also the most famous SEO company in the Bay area. Currently, we offer free website diagnosis and free consultation for limited time. To take advantage of this offer, please call 408-334-5051 and let us know the offer code: Deal. So, here are the famous google ranking factors list that Google does not want to release:
- Google Ranking Factor Domain Age: Matt Cutts states that:“The difference between a domain that’s six months old verses one year old is really not that big at all.”.In other words, they do use domain age…but it’s not very important.
- Google Ranking Factor Keyword Appears in Top Level Domain: Doesn’t give the boost that it used to, but having your keyword in the domain still acts as a relevancy signal. After all, they still bold keywords that appear in a domain name.
- Google Ranking Factor Keyword As First Word in Domain: Moz’s 2011 Search Engine Ranking Factors panelists agreed that a domain that starts with their target keyword has an edge over sites that either don’t have the keyword in their domain or have the keyword in the middle or end of their domain:Keyword starts with domain name.
- Google Ranking Factor Domain registration length: A Google patent states:“Valuable (legitimate) domains are often paid for several years in advance, while doorway (illegitimate) domains rarely are used for more than a year. Therefore, the date when a domain expires in the future can be used as a factor in predicting the legitimacy of a domain”.
- Google Ranking Factor Keyword in Subdomain Name: Moz’s panel also agreed that a keyword appearing in the subdomain boosts rank:Subdomain Keyword
- Google Ranking Factor Domain History:A site with volatile ownership (via whois) or several drops may tell Google to “reset” the site’s history, negating links pointing to the domain.
- Google Ranking Factor Exact Match Domain: EMDs may still give you an edge…if it’s a quality site. But if the EMD happens to be a low-quality site, it’s vulnerable to the EMD update.
- Google Ranking Factor Public vs. Private WhoIs: Private WhoIs information may be a sign of “something to hide”. Matt Cutts is quoted as stating at Pubcon 2006:“…When I checked the whois on them, they all had “whois privacy protection service” on them. That’s relatively unusual. …Having whois privacy turned on isn’t automatically bad, but once you get several of these factors all together, you’re often talking about a very different type of webmaster than the fellow who just has a single site or so.”
- Google Ranking Factor Penalized WhoIs Owner: If Google identifies a particular person as a spammer it makes sense that they would scrutinize other sites owned by that person.
- Google Ranking Factor Country TLD extension: Having a Country Code Top Level Domain (.cn, .pt, .ca) helps the site rank for that particular country…but limits the site’s ability to rank globally.
Other Google Ranking Factors:
- Keyword in Title Tag: The title tag is a webpage’s second most important piece of content (besides the content of the page) and therefore sends a strong on-page SEO signal.
- Title Tag Starts with Keyword: According to Moz data, title tags that starts with a keyword tend to perform better than title tags with the keyword towards the end of the tag:Title Tag Data
- Keyword in Description Tag:
Another relevancy signal. Not especially important now, but still makes a difference. - Keyword Appears in H1 Tag:
H1 tags are a “second title tag” that sends another relevancy signal to Google, according to results from this correlation study: - Keyword is Most Frequently Used Phrase in Document:
Having a keyword appear more than any other likely acts as a relevancy signal. - Content Length:
Content with more words can cover a wider breadth and are likely preferred to shorter superficial articles. SERPIQ found that content length correlated with SERP position: Content Length SEO - Keyword Density
Although not as important as it once was, keyword density is still something Google uses to determine the topic of a webpage. But going overboard can hurt you. - Latent Semantic Indexing Keywords in Content (LSI):
LSI keywords help search engines extract meaning from words with more than one meaning (Apple the computer company vs. the fruit). The presence/absence of LSI probably also acts as a content quality signal. - LSI Keywords in Title and Description Tags:
As with webpage content, LSI keywords in page meta tags probably help Google discern between synonyms. May also act as a relevancy signal. - Page Loading Speed via HTML:
Both Google and Bing use page loading speed as a ranking factor. Search engine spiders can estimate your site speed fairly accurately based on a page’s code and filesize. - Duplicate Content:
Identical content on the same site (even slightly modified) can negatively influence a site’s search engine visibility. - Rel=Canonical:
When used properly, use of this tag may prevent Google from considering pages duplicate content. - Page Loading Speed via Chrome:
Google may also use Chrome user data to get a better handle on a page’s loading time as this takes into account server speed, CDN usage and other non HTML-related site speed signals. - Image Optimization:
Images on-page send search engines important relevancy signals through their file name, alt text, title, description and caption. - Recency of Content Updates:
Google Caffeine update favors recently updated content, especially for time-sensitive searches. Highlighting this factor’s importance, Google shows the date of a page’s last update for certain pages: - Magnitude of Content Updates:
The significance of edits and changes is also a freshness factor. Adding or removing entire sections is a more significant update than switching around the order of a few words. - Historical Updates Page Updates:
How often has the page been updated over time? Daily, weekly, every 5-years? Frequency of page updates also play a role in freshness. - Keyword Prominence:
Having a keyword appear in the first 100-words of a page’s content appears to be a significant relevancy signal. - Keyword in H2, H3 Tags:
Having your keyword appear as a subheading in H2 or H3 format may be another weak relevancy signal. Moz’s panel agrees: - Keyword Word Order:
An exact match of a searcher’s keyword in a page’s content will generally rank better than the same keyword phrase in a different order. For example: consider a search for: “cat shaving techniques”. A page optimized for the phrase “cat shaving techniques” will rank better than a page optimized for “techniques for shaving a cat”. This is a good illustration of why keyword research is really, really important. - Outbound Link Quality:
Many SEOs think that linking out to authority sites helps send trust signals to Google. - Outbound Link Theme:According to Moz, search engines may use the content of the pages you link to as a relevancy signal. For example, if you have a page about cars that links to movie-related pages, this may tell Google that your page is about the movie Cars, not the automobile.
- Grammar and Spelling:Proper grammar and spelling is a quality signal, although Cutts gave mixed messages in 2011 on whether or not this was important.
- Syndicated Content:Is the content on the page original? If it’s scraped or copied from an indexed page it won’t rank as well as the original or end up in their Supplemental Index.
- Helpful Supplementary Content:According to a now-public Google Rater Guidelines Document, helpful supplementary content is an indicator of a page’s quality (and therefore, Google ranking). Examples include currency converters, loan interest calculators and interactive recipes.
- Number of Outbound Links:Too many dofollow OBLs may “leak” PageRank, which can hurt that page’s rankings.
- Multimedia:Images, videos and other multimedia elements may act as a content quality signal.
- Number of Internal Links Pointing to Page:The number of internal links to a page indicates its importance relative to other pages on the site.
- Quality of Internal Links Pointing to Page:Internal links from authoritative pages on domain have a stronger effect than pages with no or low PR.
- Broken Links:Having too many broken links on a page may be a sign of a neglected or abandoned site. The Google Rater Guidelines Document uses broken links as one was to assess a homepage’s quality.
- Reading Level:There’s no doubt that Google estimates the reading level of webpages:But what they do with that information is up for debate. Some say that a basic reading level will help your page rank because it will appeal to the masses. However, Linchpin SEO discovered that reading level was one factor that separated quality sites from content mills.
- Affiliate Links:Affiliate links themselves probably won’t hurt your rankings. But if you have too many, Google’s algorithm may pay closer attention to other quality signals to make sure you’re not a “thin affiliate site”.
- HTML errors/W3C validation:Lots of HTML errors or sloppy coding may be a sign of a poor quality site. While controversial, many in SEO think that WC3 validation is a weak quality signal.
- Page Host’s Domain Authority:All things being equal a page on an authoritative domain will higher than a page on a domain with less authority.
- Page’s PageRank:Not perfectly correlated. But in general higher PR pages tend to rank better than low PR pages.
- URL Length:Search Engine Journal notes that excessively long URLs may hurt search visibility.
- URL Path:A page closer to the homepage may get a slight authority boost.
- Human Editors:Although never confirmed, Google has filed a patent for a system that allows human editors to influence the SERPs.
- Page Category:The category the page appears on is a relevancy signal. A page that’s part of a closely related category should get a relevancy boost compared to a page that’s filed under an unrelated or less related category.
- WordPress Tags:Tags are WordPress-specific relevancy signal. According to Yoast.com:“The only way it improves your SEO is by relating one piece of content to another, and more specifically a group of posts to each other”
- Keyword in URL:Another important relevancy signal.
- URL String:The categories in the URL string are read by Google and may provide a thematic signal to what a page is about:google url strings
- References and Sources:Citing references and sources, like research papers do, may be a sign of quality. The Google Quality Guidelines states that reviewers should keep an eye out for sources when looking at certain pages: “This is a topic where expertise and/or authoritative sources are important…”.
- Bullets and Numbered Lists:Bullets and numbered lists help break up your content for readers, making them more user friendly. Google likely agrees and may prefer content with bullets and numbers.
- Priority of Page in Sitemap:The priority a page is given via the sitemap.xml file may influence ranking.
- Too Many Outbound Links:Straight from the aforementioned Quality rater document:“Some pages have way, way too many links, obscuring the page and distracting from the Main Content”
- Quantity of Other Keywords Page Ranks For:If the page ranks for several other keywords it may give Google an internal sign of quality.
- Page Age:Although Google prefers fresh content, an older page that’s regularly updated may outperform a newer page.
- User Friendly Layout:
- Citing the Google Quality Guidelines Document yet again:“The page layout on highest quality pages makes the Main Content immediately visible”
- Parked Domains:
A Google update in December of 2011 decreased search visibility of parked domains. - Useful Content:
Google may distinguish between “quality” and “useful” content. - Content Provides Value and Unique Insights:
Google has stated that they’re on the hunt for sites that don’t bring anything new or useful to the table, especially thin affiliate sites. - Contact Us Page:
The aforementioned Google Quality Document states that they prefer sites with an “appropriate amount of contact information”. Supposed bonus if your contact information matches your whois info. - Domain Trust/TrustRank:
Site trust — measured by how many links away your site is from highly-trusted seed sites — is a massively important ranking factor. You can read more about TrustRank here. - Site Architecture:
A well put-together site architecture (especially a silo structure) helps Google thematically organize your content. - Site Updates:
How often a site is updated — and especially when new content is added to the site — is a site-wide freshness factor. - Number of Pages:
The number of pages a site has is a weak sign of authority. At the very least a large site helps distinguish it from thin affiliate sites. - Presence of Sitemap:
A sitemap helps search engines index your pages easier and more thoroughly, improving visibility. - Site Uptime:
Lots of downtime from site maintenance or server issues may hurt your ranking (and can even result in deindexing if not corrected). - Server Location:
Server location may influence where your site ranks in different geographical regions. Especially important for geo-specific searches. - SSL Certificate:
Google has confirmed that they index SSL certificates and that they use HTTPS as a ranking signal. - Terms of Service and Privacy Pages:
These two pages help tell Google that a site is a trustworthy member of the internet. - Duplicate Meta Information On-Site:
Duplicate meta information across your site may bring down all of your page’s visibility.
Google Ranking Factors Continue:
- Breadcrumb Navigation:
This is a style of user-friendly site-architecture that helps users (and search engines) know where they are on a site:Both SearchEngineJournal.com and Ethical SEO Consulting claim that this set-up may be a ranking factor. - Mobile Optimized:
Google’s official stance on mobile is to create a responsive site. It’s likely that responsive sites get an edge in searches from a mobile device. In fact, they now add “Mobile friendly” tags to sites that display well on mobile devices. - YouTube:
There’s no doubt that YouTube videos are given preferential treatment in the SERPs (probably because Google owns it ):youtube resultsIn fact, Search Engine Land found that YouTube.com traffic increased significantly after Google Panda. - Site Usability:A site that’s difficult to use or to navigate can hurt ranking by reducing time on site, pages viewed and bounce rate. This may be an independent algorithmic factor gleaned from massive amounts of user data.
- Use of Google Analytics and Google Webmaster Tools:Some think that having these two programs installed on your site can improve your page’s indexing. They may also directly influence rank by giving Google more data to work with (ie. more accurate bounce rate, whether or not you get referall traffic from your backlinks etc.).
- User reviews/Site reputation:A site’s on review sites like Yelp.com and RipOffReport.com likely play an important role in the algorithm. Google even posted a rarely candid outline of their approach to user reviews after an eyeglass site was caught ripping off customers in an effort to get backlinks.
- Linking Domain Age:Backlinks from aged domains may be more powerful than new domains.
- # of Linking Root Domains:The number of referring domains is one of the most important ranking factors in Google’s algorithm, as you can see from this chart from Moz (bottom axis is SERP position).
- # of Links from Separate C-Class IPs:Links from seperate class-c IP addresses suggest a wider breadth of sites linking to you.
- # of Linking Pages:The total number of linking pages — even if some are on the same domain — is a ranking factor.
- Alt Tag (for Image Links):
Alt text is an image’s version of anchor text. - Links from .edu or .gov Domains:
Matt Cutts has stated that TLD doesn’t factor into a site’s importance. However, that doesn’t stop SEOs from thinking that there’s a special place in the algo for .gov and .edu TLDs. - Authority of Linking Page:
The authority (PageRank) of the referring page is an extremely important ranking factor. - Authority of Linking Domain:The referring domain’s authority may play an independent role in a link’s importance (ie. a PR2 page link from a site with a homepage PR3 may be worth less than a PR2 page link from PR8 Yale.edu).
- Links From Competitors:Links from other pages ranking in the same SERP may be more valuable for a page’s rank for that particular keyword.
- Social Shares of Referring Page:The amount of page-level social shares may influence the link’s value.
- Links from Bad Neighborhoods:Links from “bad neighborhoods” may hurt your site.
- Guest Posts:Although guest posting can be part of a white hat SEO campaign, links coming from guest posts — especially in an author bio area — may not be as valuable as a contextual link on the same page.
- Links to Homepage Domain that Page Sits On:Links to a referring page’s homepage may play special importance in evaluating a site’s — and therefore a link’s — weight.
- Nofollow Links:One of the most controversial topics in SEO. Google’s official word on the matter is:“In general, we don’t follow them.”Which suggests that they do…at least in certain cases. Having a certain % of nofollow links may also indicate a natural vs. unnatural link profile.
- Diversity of Link Types:
Having an unnaturally large percentage of your links come from a single source (ie. forum profiles, blog comments) may be a sign of webspam. On the other hand, links from diverse sources is a sign of a natural link profile. - “Sponsored Links” Or Other Words Around Link:
Words like “sponsors”, “link partners” and “sponsored links” may decrease a link’s value. - Contextual Links:
Links embedded inside a page’s content are considered more powerful than links on an empty page or found elsewhere on the page.contextual backlinkA good example of contextual links are backlinks from guestographics. - Excessive 301 Redirects to Page:
Links coming from 301 redirects dilute some (or even all) PR, according to a Webmaster Help Video. - Backlink Anchor Text:As noted in this description of Google’s original algorithm:“First, anchors often provide more accurate descriptions of web pages than the pages themselves.”Obviously, anchor text is less important than before (and likely a webspam signal). But it still sends a strong relevancy signal in small doses.
- Internal Link Anchor Text:Internal link anchor text is another relevancy signal, although probably weighed differently than backlink anchor text.
- Link Title Attribution:The link title (the text that appears when you hover over a link) is also used as a weak relevancy signals.
- Country TLD of Referring Domain:Getting links from country-specific top level domain extensions (.de, .cn, .co.uk) may help you rank better in that country.
- Link Location In Content:Links in the beginning of a piece of content carry slight more weight than links placed at the end of the content.
- Link Location on Page: Where a link appears on a page is important. Generally, links embedded in a page’s content are more powerful than links in the footer or sidebar area.
- Linking Domain Relevancy:
A link from site in a similar niche is significantly more powerful than a link from a completely unrelated site. That’s why any effective SEO strategy today focuses on obtaining relevant links. - Page Level Relevancy:
The Hilltop Algorithm states that link from a page that’s closely tied to page’s content is more powerful than a link from an unrelated page. - Text Around Link Sentiment:
Google has probably figured out whether or not a link to your site is a recommendation or part of a negative review. Links with positive sentiments around them likely carry more weight. - Keyword in Title:
Google gives extra love to links on pages that contain your page’s keyword in the title (“Experts linking to experts”.) - Positive Link Velocity:
A site with positive link velocity usually gets a SERP boost. - Negative Link Velocity:
Negative link velocity can significantly reduce rankings as it’s a signal of decreasing popularity. - Links from “Hub” Pages:
Aaron Wall claims that getting links from pages that are considered top resources (or hubs) on a certain topic are given special treatment. - Link from Authority Sites:
A link from a site considered an “authority site” likely pass more juice than a link from a small, microniche site. - Linked to as Wikipedia Source:
Although the links are nofollow, many think that getting a link from Wikipedia gives you a little added trust and authority in the eyes of search engines. - Co-Occurrences:
The words that tend to appear around your backlinks helps tell Google what that page is about. - Backlink Age:
According to a Google patent, older links have more ranking power than newly minted backlinks. - Links from Real Sites vs. Splogs:
Due to the proliferation of blog networks, Google probably gives more weight to links coming from “real sites” than from fake blogs. They likely use brand and user-interaction signals to distinguish between the two. - Natural Link Profile:
A site with a “natural” link profile is going to rank highly and be more durable to updates. - Reciprocal Links:
Google’s Link Schemes page lists “Excessive link exchanging” as a link scheme to avoid. - User Generated Content Links:
Google is able to identify links generated from UGC vs. the actual site owner. For example, they know that a link from the official WordPress.com blog at en.blog.wordpress.com is very different than a link from besttoasterreviews.wordpress.com. - Links from 301:
Links from 301 redirects may lose a little bit of juice compared to a direct link. However, Matt Cutts says that a 301 is similar to a direct link. - Schema.org Microformats:
Pages that support microformats may rank above pages without it. This may be a direct boost or the fact that pages with microformatting have a higher SERP CTR:microformats - DMOZ Listed:
Many believe that Google gives DMOZ listed sites a little extra trust. - TrustRank of Linking Site:
The trustworthiness of the site linking to you determines how much “TrustRank” gets passed onto you. - Number of Outbound Links on Page:
PageRank is finite. A link on a page with hundreds of OBLs passes less PR than a page with only a few OBLs. - Forum Profile Links:
Because of industrial-level spamming, Google may significantly devalue links from forum profiles. - Word Count of Linking Content:
A link from a 1000-word post is more valuable than a link inside of a 25-word snippet. - Quality of Linking Content:
Links from poorly written or spun content don’t pass as much value as links from well-written, multimedia-enhanced content. - Sitewide Links:
Matt Cutts has confirmed that sitewide links are “compressed” to count as a single link. - Organic Click Through Rate for a Keyword:
Pages that get clicked more in CTR may get a SERP boost for that particular keyword. - Organic CTR for All Keywords:
A page’s (or site’s) organic CTR for all keywords is ranks for may be a human-based, user interaction signal. - Bounce Rate:
Not everyone in SEO agrees bounce rate matters, but it may be a way of Google to use their users as quality testers (pages where people quickly bounce is probably not very good). - Direct Traffic:
It’s confirmed that Google uses data from Google Chrome to determine whether or not people visit a site (and how often). Sites with lots of direct traffic are likely higher quality than sites that get very little direct traffic. - Repeat Traffic:
They may also look at whether or not users go back to a page or site after visiting. Sites with repeat visitors may get a Google ranking boost. - Blocked Sites:
Google has discontinued this feature in Chrome. However, Panda used this feature as a quality signal. - Chrome Bookmarks:
We know that Google collects Chrome browser usage data. Pages that get bookmarked in Chrome might get a boost. - Google Toolbar Data:
Search Engine Watch’s Danny Goodwin reports that Google uses toolbar data as a ranking signal. However, besides page loading speed and malware, it’s not known what kind of data they glean from the toolbar.
More Google Ranking Factors:
- Number of Comments:
Pages with lots of comments may be a signal of user-interaction and quality. - Dwell Time:
Google pays very close attention to “dwell time”: how long people spend on your page when coming from a Google search. This is also sometimes referred to as “long clicks vs short clicks”. If people spend a lot of time on your site, that may be used as a quality signal. - Query Deserves Freshness:
Google gives newer pages a boost for certain searches. - Query Deserves Diversity:
Google may add diversity to a SERP for ambiguous keywords, such as “Ted”, “WWF” or “ruby”. - User Browsing History:
Sites that you frequently visit while signed into Google get a SERP bump for your searches. - User Search History:
Search chain influence search results for later searches. For example, if you search for “reviews” then search for “toasters”, Google is more likely to show toaster review sites higher in the SERPs. - Geo Targeting:
Google gives preference to sites with a local server IP and country-specific domain name extension. - Safe Search:
Search results with curse words or adult content won’t appear for people with Safe Search turned on. - Google+ Circles:
Google shows higher results for authors and sites that you’ve added to your Google Plus Circles - DMCA Complaints:
Google “downranks” pages with DMCA complaints. - Domain Diversity:
The so-called “Bigfoot Update” supposedly added more domains to each SERP page. - Transactional Searches:
Google sometimes displays different results for shopping-related keywords, like flight searches. - Local Searches:
Google often places Google+ Local results above the “normal” organic SERPs. - Google News Box:
Certain keywords trigger a Google News box: - Big Brand Preference:
After the Vince Update, Google began giving big brands a boost for certain short-tail searches. - Shopping Results:
Google sometimes displays Google Shopping results in organic SERPs: - Image Results:
Google elbows our organic listings for image results for searches commonly used on Google Image Search. - Easter Egg Results:
Google has a dozen or so Easter Egg results. For example, when you search for “Atari Breakout” in Google image search, the search results turn into a playable game (!). Shout out to Victor Pan for this one. - Single Site Results for Brands:
Domain or brand-oriented keywords bring up several results from the same site. - Number of Tweets:
Like links, the tweets a page has may influence its rank in Google. - Authority of Twitter Users Accounts:
It’s likely that Tweets coming from aged, authority Twitter profiles with a ton of followers (like Justin Bieber) have more of an effect than tweets from new, low-influence accounts. - Number of Facebook Likes:
Although Google can’t see most Facebook accounts, it’s likely they consider the number of Facebook likes a page receives as a weak ranking signal. - Facebook Shares:
Facebook shares — because they’re more similar to a backlink — may have a stronger influence than Facebook likes. - Authority of Facebook User Accounts:
As with Twitter, Facebook shares and likes coming from popular Facebook pages may pass more weight. - Pinterest Pins:
Pinterest is an insanely popular social media account with lots of public data. It’s probably that Google considers Pinterest Pins a social signal. - Votes on Social Sharing Sites:
It’s possible that Google uses shares at sites like Reddit, Stumbleupon and Digg as another type of social signal. - Number of Google+1’s:
Although Matt Cutts gone on the record as saying Google+ has “no direct effect” on rankings, it’s hard to believe that they’d ignore their own social network. - Authority of Google+ User Accounts:
It’s logical that Google would weigh +1’s coming from authoritative accounts more than from accounts without many followers. - Known Authorship:
In February 2013, Google CEO Eric Schmidt famously claimed:“Within search results, information tied to verified online profiles will be ranked higher than content without such verification, which will result in most users naturally clicking on the top (verified) results.”Although the Google+ authorship program has been shut down, it’s likely Google uses some form of authorship to determine influential content producers online (and give them a boost in rankings). - Social Signal Relevancy:
Google probably uses relevancy information from the account sharing the content and the text surrounding the link. - Site Level Social Signals:
Site-wide social signals may increase a site’s overall authority, which will increase search visibility for all of its pages. - Brand Name Anchor Text:
Branded anchor text is a simple — but strong — brand signal. - Branded Searches:
It’s simple: people search for brands. If people search for your site in Google (ie. “Backlinko twitter”, Backlinko + “ranking factors”), Google likely takes this into consideration when determining a brand. - Site Has Facebook Page and Likes:
Brands tend to have Facebook pages with lots of likes. - Site has Twitter Profile with Followers:
- Official Linkedin Company Page:
Most real businesses have company Linkedin pages. - Employees Listed at Linkedin:
Rand Fishkin thinks that having Linkedin profiles that say they work for your company is a brand signal. - Legitimacy of Social Media Accounts:
A social media account with 10,000 followers and 2 posts is probably interpreted a lot differently than another 10,000-follower strong account with lots of interaction. - Brand Mentions on News Sites:
Really big brands get mentioned on Google News sites all the time. In fact, some brands even have their own Google News feed on the first page: - Co-Citations:
Brands get mentioned without getting linked to. Google likely looks at non-hyperlinked brand mentions as a brand signal. - Number of RSS Subscribers:
Considering that Google owns the popular Feedburner RSS service, it makes sense that they would look at RSS Subscriber data as a popularity/brand signal. - Brick and Mortar Location With Google+ Local Listing:
Real businesses have offices. It’s possible that Google fishes for location-data to determine whether or not a site is a big brand. - Website is Tax Paying Business:
Moz reports that Google may look at whether or not a site is associated with a tax-paying business. - Panda Penalty:
Sites with low-quality content (particularly content farms) are less visible in search after getting hit by a Panda penalty. - Links to Bad Neighborhoods:
Linking out to “bad neighborhoods” — like pharmacy or payday loan sites — may hurt your search visibility. - Redirects:
Sneaky redirects is a big no-no. If caught, it can get a site not just penalized, but de-indexed. - Popups or Distracting Ads:
The official Google Rater Guidelines Document says that popups and distracting ads is a sign of a low-quality site. - Site Over-Optimization:
Includes on-page factors like keyword stuffing, header tag stuffing, excessive keyword decoration. - Page Over-Optimizaton:
Many people report that — unlike Panda — Penguin targets individual page (and even then just for certain keywords). - Ads Above the Fold:
The “Page Layout Algorithm” penalizes sites with lots of ads (and not much content) above the fold. - Hiding Affiliate Links:
Going too far when trying to hide affiliate links (especially with cloaking) can bring on a penalty. - Affiliate Sites:
It’s no secret that Google isn’t the biggest fan of affiliates. And many think that sites that monetize with affiliate links are put under extra scrutiny. - Autogenerated Content:
Google isn’t a big fan of autogenerated content. If they suspect that your site’s pumping out computer-generated content, it could result in a penalty or de-indexing. - Excess PageRank Sculpting:
Going too far with PageRank sculpting — by nofollowing all outbound links or most internal links — may be a sign of gaming the system. - IP Address Flagged as Spam:
If your server’s IP address is flagged for spam, it may hurt all of the sites on that server. - Meta Tag Spamming:
Keyword stuffing can also happen in meta tags. If Google thinks you’re adding keywords to your meta tags to game the algo, they may hit your site with a penalty. - Unnatural Influx of Links:
A sudden (and unnatural) influx of links is a sure-fire sign of phony links. - Penguin Penalty:Sites that were hit by Google Penguin are significantly less visible in search.
- Link Profile with High % of Low Quality Links:
Lots of links from sources commonly used by black hat SEOs (like blog comments and forum profiles) may be a sign of gaming the system. - Linking Domain Relevancy:
The famous analysis by MicroSiteMasters.com found that sites with an unnaturally high amount of links from unrelated sites were more susceptible to Penguin. - Unnatural Links Warning:
Google sent out thousands of “Google Webmaster Tools notice of detected unnatural links” messages. This usually precedes a ranking drop, although not 100% of the time. - Links from the Same Class C IP:
Getting an unnatural amount of links from sites on the same server IP may be a sign of blog network link building. - “Poison” Anchor Text:
Having “poison” anchor text (especially pharmacy keywords) pointed to your site may be a sign of spam or a hacked site. Either way, it can hurt your site’s ranking. - Manual Penalty:
Google has been known to hand out manual penalties, like in the well-publicized Interflora fiasco. - Selling Links:
Selling links can definitely impact toolbar PageRank and may hurt your search visibility. - Google Sandbox:
New sites that get a sudden influx of links are sometimes put in the Google Sandbox, which temporarily limits search visibility. - Google Dance:
The Google Dance can temporarily shake up rankings. According to a Google Patent, this may be a way for them to determine whether or not a site is trying to game the algorithm. - Disavow Tool:
Use of the Disavow Tool may remove a manual or algorithmic penalty for sites that were the victims of negative SEO. - Reconsideration Request:
A successful reconsideration request can lift a penalty. - Temporary Link Schemes:
Google has (apparently) caught onto people that create — and quickly remove — spammy links. Also know as a temporary link scheme.
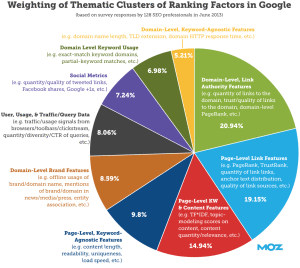
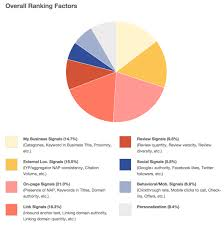
This was the complete list of Google Ranking Factors. Thanks to Moz that they summarized most of these ranking factors on the picture below:
In conclusion, good SEO (search engine optimization) means paying attention to Google Ranking Factors. This is the only way to improve Google SEO Ranking. Since most people search on Google and 80% of people who search on Google click organic listings (20% is PPC), it makes a great sense to pay attention to these Google Ranking Factors.
SEO San Jose is a SEO (Search Engine Optimization) company based in San Jose, San Francisco and San Leandro. San Jose SEO Company, SEO San Jose offers San Jose SEO (Search Engine Optimization), search engine marketing (SEM), pay per click marketing (PPC), website design and development, content marketing and social media marketing services. In order to get the best San Jose SEO services, call the best San Jose SEO Company SEO San Jose:
San Jose SEO by SEO San Jose – 89 Wabash Ave, Unit 5, San Jose, CA, 95128 – Phone: (408) 334-5051 – Email: info@seo-san-jose.net